Typical section showing key components
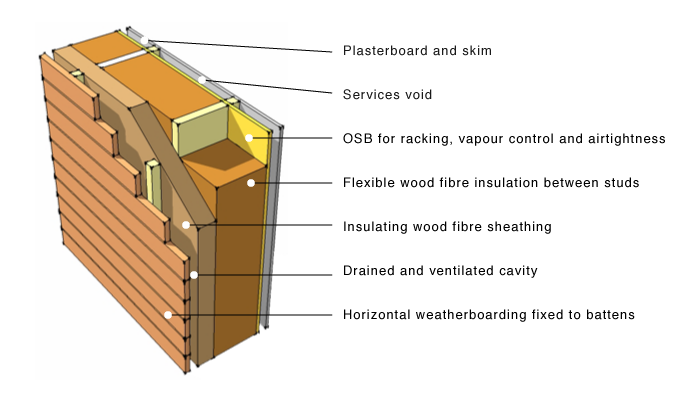
This section shows the key components involved in maximising the application of wood fibre insulation in a typical timber frame scenario. The service of racking the timber frame is provided by the OSB attached to the internal face of the studwork. The OSB also doubles as an important vapour control and airtightness layer. The layer is protected from penetration by pulling services into a zone formed by battens and the inner board. Flexible insulation is friction-fitted between the studs and a further layer of more compressed water-resistant wood fibre boarding forms the protective sheathing. Cladding of choice (attached to the frame) is mounted on battens attached through to the studwork.
This is a good example of the traditional 'breathing' construction though consistent inclusion of materials outside of the vapour control layer that are vapour permeable and hygroscopic (alternative between-stud insulation materials such as hemp or sheep wool could also be considered). The function of a traditional breather membrane is replaced by the external layer of wood fibre sheathing.
As with all types of construction requiring high standards of air tightness, care needs to be taken in the detailing of the OSB junctions - tape will need to be used and the whole inspected carefully before any covering up.
Although the section is quite deep compared with application using petrochemically derived insulation, the extensive use of wood can significantly reduce the levels of embodied energy.
Examples of low u-value applications
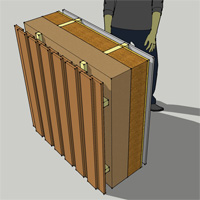
OSB / timber frame / sheathing / horizontal timber boarding• 12.5mm plasterboard and skim • 38mm service void • 15mm OSB racking/air tightness/vapour control (0.13 W/mK) • 220mm stud frame infilled with flexible woodfibre batts (0.038 W/mK) • 80mm rigid wood fibre sheathing (0.043 W/mK) • Ventilated cavity • Horizontal timber board cladding Approx U-value = 0.14 (subject to specification) |
|
 |
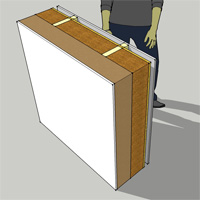
OSB / timber frame / sheathing / vertical timber boarding• 12.5mm plasterboard and skim • 38mm service void • 15mm OSB racking/air tightness/vapour control (0.13 W/mK) • 140mm stud frame infilled with flexible woodfibre batts (0.038 W/mK) • 160mm rigid wood fibre sheathing (0.043 W/mK) • Ventilated cavity • Vertical timber board cladding Approx U-value = 0.13 (subject to specification) |
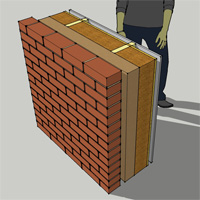 |
OSB / timber frame / sheathing / brick cladding• 12.5mm plasterboard and skim • 38mm service void • 15mm OSB racking/air tightness/vapour control (0.13 W/mK) • 140mm stud frame infilled with flexible woodfibre batts (0.038 W/mK) • 100mm rigid wood fibre sheathing (0.043 W/mK) • 50mm ventilated cavity • Brick cladding Approx U-value = 0.15 (subject to specification |
 |
OSB / timber frame / sheathing / render• 12.5mm plasterboard and skim • 38mm service void • 15mm OSB racking/air tightness/vapour control (0.13 W/mK) • 140mm stud frame infilled with flexible woodfibre batts (0.038 W/mK) • 140mm rigid wood fibre insulation (0.043 W/mK) • Lime or polymer (vapour permeable) render Approx U-value = 0.15 (subject to specification) |
Disclaimer
GreenSpec accepts no responsibility or liability for any damages or costs of any type arising out of or in any way connected with your use of this web site. Data and information is provided for information purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither GreenSpec nor any of its partners shall be liable for any errors in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon.
